Measuring opportunity cost in statistics using evaluative space grid items: results from a pilot study
Abstract
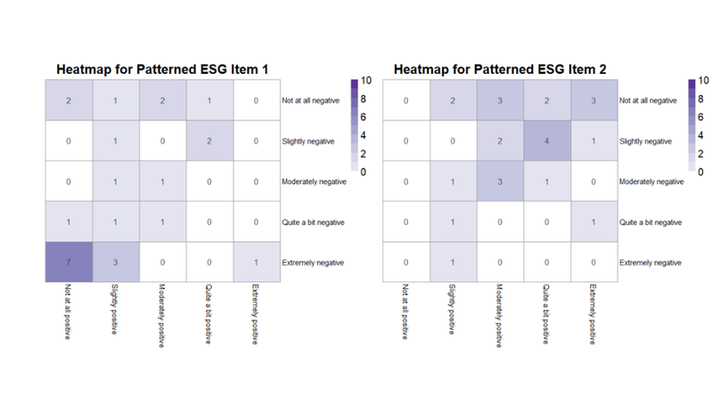
Challenges to measuring students’ attitudes toward statistics remain despite decades of focused research. Measuring the expectancy-value theory (EVT) Cost construct has been especially challenging owing in part to the historical lack of research about it. To measure the EVT Cost construct better, this study asked university students to respond to items using both a Likert-type response and an Evaluative Space Grid (ESG)-type response. ESG items enable bivariate responses in a single item and permit distinguishing among two different types of neutral attitudes: indifferent and ambivalent. This pilot study evaluates the appropriateness of ESG-type items for measuring the EVT Cost construct by analyzing student response patterns to ESG-type items and comparing them with Likert-type items. Validity evidence is documented using descriptive statistics and graphs, correlations among items, and a trinomial hypothesis test. Internal consistency reliability indices are also reported. Friedman’s Test is used to compare the average response times for items of different types. Results indicate that students can meaningfully respond to ESG-type items in ways that are similar to their Likert-type responses, that students respond to ESG-type items quicker with more practice, and that distinguishing among indifferent and ambivalent attitudes seems appropriate for the EVT Cost construct. These findings suggest that ESG-type items may provide new insights not possible with Likert-type items but also that more research should be conducted to better understand their advantages and disadvantages within statistics education.